Social Token as Financial Assets (Blue Version)
Social Tokens allow you to unlock different experiences with your community. Every audience will turn into a community, and every fan will turn into a partner. With Social tokens, you'll have the power to incentivize anyone to help you achieve broader goals, meet new people and collaborate with others. You'll finally have a direct relationship with your community and create new kinds of experiences instead of relying on centralized platforms that can potentially ban or censor your work at any time.
With Social Token used purely for its utility, your tokens can thrive in a niche community even though it has no monetary value. It's more of a social, collectible value that people are proud to own. But to create real incentives around a joint project, the financial value of a Token has its importance.
Indeed to create a whole new economy where every individual can thrive, we need creators to collaborate, and social tokens have shown their efficiency to incentivize individuals to share their skills with others. Financial aspects of Social Tokens are more than crucial as well-designed incentives can make your project tremendously grow. Remember that the more value your Token will have, the easiest it will be to incentivize contributors to participate.
There are two main ways to create a Token. The first one is to make your Token on a Fixed Supply Model; you're creating a fixed supply of Token, the standard is 10M, and you can then distribute it to whoever you want in the way you want. The second one is to create it on a Bonding Curve Model; you're creating your Token on a Bonding Curve, which means the supply starts at 0, and every new Token created will cost more than the previous one.
There is no right or wrong answer, but there are fundamental differences between creating on a Bonding curve and a fixed supply, and it's essential to understand those differences well to make sure it fits your needs.
Today, we'll explain the main differences between a bonding curve model and a Fixed Supply model and which one you should choose for your project. 🔥
1 - The Fixed Supply Model
The fixed supply model is a model where you define the number of tokens you want to create beforehand. Having a fixed supply allows you to get directly in your Crypto Wallet a known number of tokens that you can share or give to incentivize your community to participate in your project. The industry standard is to create 10 million of your tokens, but you can define the number of tokens you want to create. Successful communities such as Friends With Benefits or MetaFactory have minted (created) respectively only 1 million and 420k of their Token. Creating your Token on a Fixed Supply means you have full power over the distribution of the native Token.
$FF distribution by Forefront - the token has been minted on a 10M Fixed Supply.
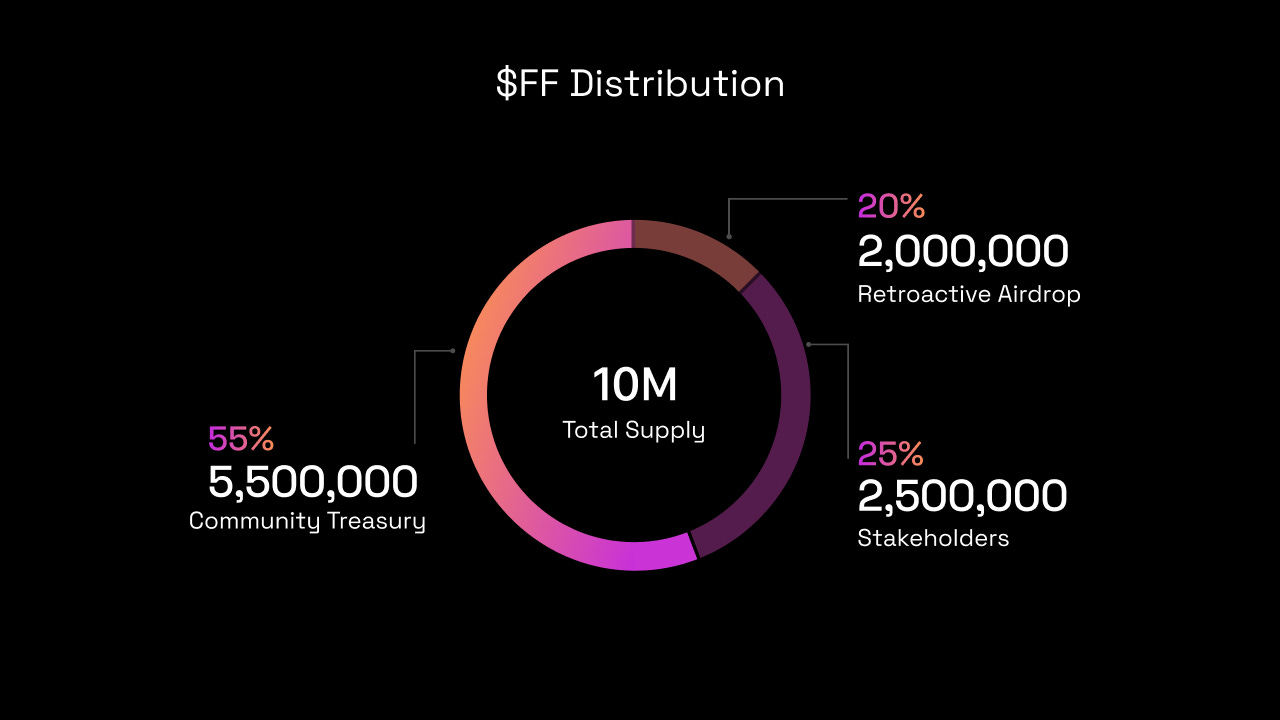
The fixed supply model works more around personal tokens. If you're a Creator that wants an easy solution to experiment with Social Token and create new experiences with your fan, you should hands-down mint your Token on a fixed supply.
However, in creating your Token on a Fixed Supply, you'll be limited at one point if your project grows exponentially as you won't be able to increase the supply. It's also good to remember that when building on a Fixed supply, your Token has no inherent value as you're the owner of most of the supply, and no one has put money into your project. With a token based on a fixed supply, you'll create experiences that don't require inherent value. Experiences that only live in your economy. We could think of a "control my life" type of experience, gated articles or content (your fans will need enough of your Token to read the article), tips for spontaneous help, etc.
But creating your Token on a fixed supply doesn't mean it will never have monetary value, and you can create a Liquidity Pool, set an initial price, and allow anyone to buy your Token.
Adding value to your Token is not the first thing you should do when creating one. Indeed, you should first focus on making actual use cases for your Token and gather a strong community around your project. Without a strong community, you won't increase your Token's value as no one will be keen to buy it. Creating a liquidity pool is more a later stage action when you'll want to accomplish new (and maybe more significant) projects than part of the initial tasks you should make when creating a token.
Let's get into the fun part of Social Tokens: The liquidity Pools (LP).
(If you want to understand more in-depth the advantages of creating a Social Token on a Fixed Supply, you can read the more extended version of this essay).
2 - Liquidity Pool
2.1 - What is a liquidity Pool?
Put simply, creating a Liquidity pool means providing Liquidity for potential buyers. When you're creating a social Token, this Token has no inherent value. Creating a liquidity pool (LP) allows anyone to buy your Token in exchange for other cryptocurrencies with value in USD. When the LP is created, users can add the exact value of two Token (your Token + collateral, aka any other token) in a Pool and earn trading fees proportional to their share of the total Liquidity.
Users putting Liquidity in a pool are named Liquidity Providers, and they make a % of fees on every trade in the pools they participate in and are therefore incentivized to add Liquidity. Put simply, these Liquidity providers facilitate trading by willing to buy or sell a particular asset at any given time, thereby providing Liquidity and enabling traders to trade without waiting for another buyer or seller to show up.
2.2 - So why would you need to pool Liquidity for your Token?
You will need to pool Liquidity if you want to create a project that requires collaboration. By pooling liquidity, you'll drive the value of your Token, define its price and allow anyone to purchase it. Believers of your project will have the power to participate by simply swapping (exchanging) any crypto for your Token. They'll be able to buy your Token by simply going on a decentralized exchange and type the name of your Token.
Uniswap (decentralized exchange) interface
While centralized exchanges match buyers and sellers to determine prices and execute trades, taking a fee on the transaction, Uniswap uses a simple math equation and pools of tokens and ETH to do the same job. By knowing the balance between the ETH and your $NAME token in a pool (Supply & demand), the equation can determine the price of a particular token whenever someone buys your $NAME Token with ETH. If your $NAME Token supply decreases while the Supply of ETH increases, your $NAME token price goes up. Your Token now has a monetary value.
Also, by creating a Liquidity Pool, you'll create a place where anyone can buy your token and therefore participate in the project you're building. It will give ownership to your fans and, as the value of your token increases (considering more people are buying it and assuming you still own a decent amount of your Token), you'll get more money to realize your project.
However, suppose you're creating a community around a vision (e.g., BanklessDAO) or building a protocol (e.g., Rarible protocol or Zora). In that case, it might be preferable to create your Token on a Bonding curve.
(If you want to understand better the mechanisms of liquidity pools and explore more use cases, you can read the longer version of this essay.)
3 - The Bonding Curve Model
The core idea of minting a token on a bonding curve is that its price increases as the Supply or distribution of the Token do. The more tokens have been distributed, the higher the price. This means that early adopters can buy the Token at a much cheaper rate than when the Supply increases over time.
Let's take an example to illustrate what a bonding curve is. You've just launched your Token on a Bonding curve, and your best friend John wants to buy some. To make it easier, let's say that your Token is on a classic (linear) bonding curve and that the price of the first Token is $1. John will pay $1 for the first Token, $2 for the second, for the third, $3, and so on. This means for John to get the first ten tokens, he will have to pay $1+$2+$3+$4+$5. Totaling at $55.
Now, let's say your Mom wants to buy ten tokens. Your Mom's tokens price won't start at $1 but at $11 (as John already purchased the first ten tokens). Every new buyer pushed the price up by increasing the Supply.
On the other hand, when someone sells a Token, it will be burnt (destroyed), decrease the Supply, and lower the Token price. People that have bought your Token early (at a low price) and have believed early in your project will be rewarded by being able to resell their Token at a Higher price as the price is increasing with the Supply (the more people believing in your project, the more the price of your Token will increase).
Creating your Token on a bonding curve greatly facilitates giving value to the token and allowing you to determine how the discovery price will work in the future. Indeed, a bonding curve has its own AMM (Automated Market Maker - a mathematical function that defines the price of your Token depending on different parameters) that allows you to choose the best model of bonding curve depending on your needs. You have way more freedom over the price discovery of your Token with a token minted on a bonding curve than on a fixed supply, and you can choose the type of bonding curve you want, depending on your needs.
(There are different types of bonding curves, and it might be helpful to dig into those if you're interested in creating a Token on a Bonding Curve. You can read the more extended version of this essay where we go cover those questions).
4 - Recap & Closing thoughts
Now that we've covered what a Fixed supply model, a liquidity pool, and a Bonding curve are, you should clearly understand the differences between them.
As mentioned before, the fixed supply model and the bonding curve model are entirely different and are not made for the same use cases.
To make it easier to understand, we'll make a quick recap here covering the main differences between the fixed Supply and the bonding curve models and the pros and cons of each model.
Main advantages of creating your Social Token on a Fixed Supply model :
- Usability and lower barrier to entry. Anyone can create its Token on a Fixed Supply. You'll receive the tokens in your Crypto Wallet and can then distribute them the way you want. You don't technically need a pre-existing community willing to buy your first tokens. They are already created and exist on the blockchain. You own the whole Supply from day 1.
- Full power over the distribution of the native Token. Centralized control over your token Supply prevents anyone from buying a significant amount of your token and using them in a harmful way. A safe and sustainable distribution strategy is critical for some projects - you must get your Token into the right people's hands if you want the project to succeed.
- Easier if you're a solo creator creating a personal token. The Fixed Supply model will allow you to take your time and think thoroughly about the way you want to build your project. By owning the whole Supply, you can allocate your tokens the way you want.
- You don't need a strong community that is ready to pay from day one. As you own the total Supply, you can take your time to gather a strong community around a joint project. This is a great advantage compared to the Bonding curve model as, in the bonding curve model, the early adopters might buy the Token. Still, if the community is not big and strong enough, as the price rises, no one will buy tokens anymore and can kill the project.
Main advantages of creating your Social Token on a Bonding Curve model :
- Guaranteed Liquidity: you can create a contract and have anyone be able to buy and sell your token right away. It can help bootstrap awareness and interest as backers know they have Liquidity from day one. Tokens can be purchased or sold instantaneously as the bonding curve act as an automated market maker (Market makers are agents that alleviate this problem by facilitating trade that would otherwise not occur. "Automated market makers" (AMMs) are algorithmic agents that perform those functions and, as a result, provide Liquidity in electronic markets. AMM buys some of your tokens and agrees to sell them at any given time to anyone wanting to buy your Token.)
- Reduced volatility: in times of changing demand for the Token, the bonding curve allows both the price and Supply to adjust in response. Deterministic price calculation decreases the size and probability of boom and bust cycles that frequently plague fixed-supply tokens. Also, it ensures a continuous price. The price of your Token will always be n-1
- Limitless Supply. There is no limit to the number of tokens that can be minted. You have no limits on how big your project can become.
- You have complete power over the future discovery price of your Token. As seen in this essay, you can adapt it depending on your needs.
- Reduces the risks of hacks. If your platform or project is hacked, as you don't own all the Supply, it limits the risks. Tokens belong to the users that bought them and are on their wallets.
- Easier for a protocol or a community with more options. You usually don't know the Supply you need as you don't know if your project will grow exponentially. With a bonding curve, as long as there is demand, it will be possible to create new tokens.
If you want an easy solution for your personal Token, you should go with a fixed supply model for your Token. On the other hand, if you're a big community founder or the Creator of a protocol that wants to launch a token, maybe you should consider creating a bonding curve and exploring the pros and cons of the different types of bonding curves.

